Network Status
Check the network status on the web Status > Basic > Network Information interface.
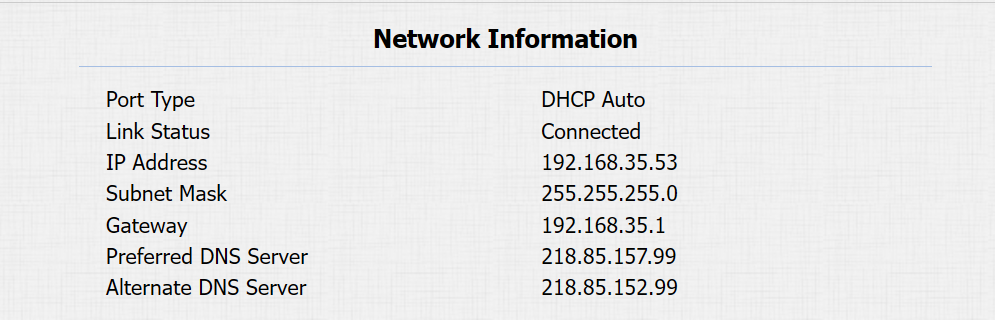
Device Network Configuration
To ensure normal functioning, make sure that the device has its IP address set correctly or obtained automatically from the DHCP server.
To set it up, go to the Network > Basic interface.
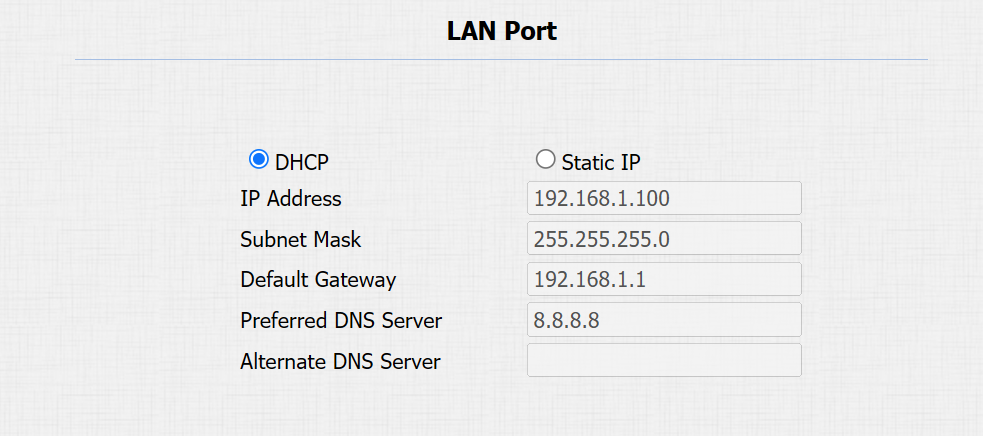
DHCP: DHCP mode is the default network connection. If the DHCP mode is turned on, the device will automatically be assigned by the DHCP server with an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server address.
Static IP: The IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server address have to be manually configured according to the actual network environment.
IP Address: Set up the IP address when the static IP mode is selected. To access the device’s web settings with the IP address, your computer should be on the same local network as the device.
Subnet Mask: A subnet mask tells your device which IP addresses are part of your local network and which ones are not. For example, if the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, it means that devices with similar starting IPs (like 192.168.1.x) are in the same network.
Default Gateway: The gateway is like a bridge between your device and other networks, such as the internet. Usually, it’s the IP address of your router.
Preferred & Alternate DNS Server: Domain Name System(DNS) is the overall system or network that handles the translation of domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses (like 192.0.2.1), which computers use to identify each other on a network. The door phone connects to the alternate DNS server when the primary one is unavailable.
Device Deployment in Network
To facilitate device control and management, configure Akuvox intercom devices with details such as location, operation mode, address, and extension numbers.
To set it up, go to the Network > Advanced > Connect Setting interface.
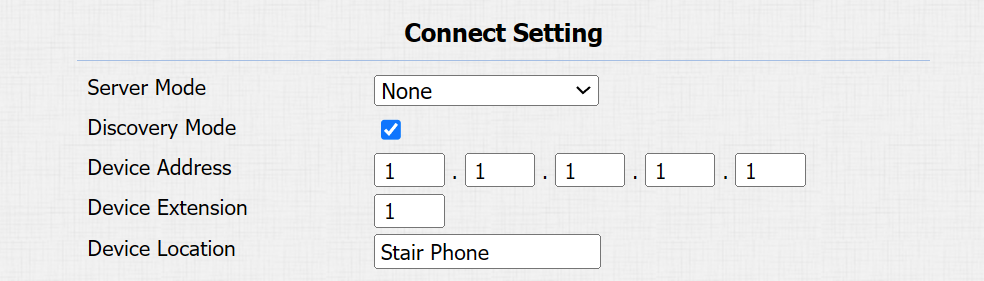
Server Mode: It is automatically set up according to the actual device connection with a specific server in the network, such as SDMC, Cloud, or None.
None: None is the default factory setting, indicating the device is not in any server type. Devices connect directly to each other or within a local area network (LAN) without relying on external servers.
Cloud: The device is connected to the SmartPlus Cloud, a cloud-based system simplifying property access management. The Cloud mode allows devices to interact intelligently with one another and the mobile SmartPlus App, backing up data daily and on different hosts. It suits projects requiring smart, flexible, and secure deployment and management.
SDMC: The device is connected to the SDMC, a management platform designed for on-premise projects. The SDMC mode manages and backs up data remotely on a local network. It also boasts many features suitable for projects requiring high privacy, lower cost, and centralized management.
Discovery Mode: With discovery mode enabled, the device can be discovered by other devices in the network. Uncheck the box if you want to conceal the device.
Device Address: Specify the device address by entering device location info from left to right: Community, Building, Unit, Floor, and Room in sequence.
Device Extension: The device extension number.
Device Location: The location where the device is installed and used.
Device Local RTP Configuration
Real-time Transport Protocol(RTP) lets devices stream audio and video data over a network in real time.
To use RTP, devices need a range of ports. A port is like a channel for data on a network. By setting up RTP ports on your device and router, you can avoid network interference and improve audio and video quality.
To set it up, go to the Network > Advanced > Local RTP interface.
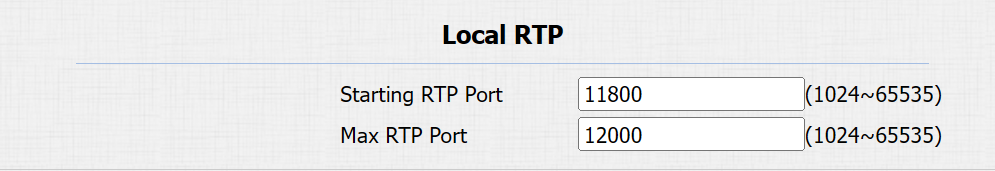
Starting RTP Port: The port value to establish the start point for the exclusive data transmission range.
Max RTP port: The port value to establish the endpoint for the exclusive data transmission range.
NAT Setting
Network Address Translation(NAT) lets devices on a private network use a single public IP address to access the internet or other public networks. NAT saves the limited public IP addresses and hides the internal IP addresses and ports from the outside world.
To register SIP accounts on third-party servers in a Wide Area Network(WAN), you need to enable the RPort feature on the intercom devices to establish a stable connection.
To set up NAT, navigate to the Account > Basic > NAT interface.
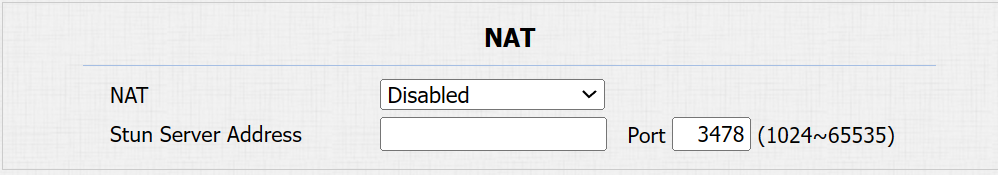
Stun Server Address: Set the SIP server address in the Wide Area Network(WAN).
Port: Set the SIP server port.
Then set up NAT on the Account > Advanced > NAT interface.
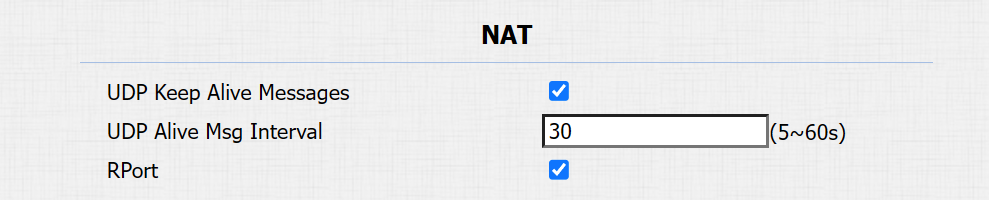
UDP Keep Alive Messages: If enabled, the device will send out the message to the SIP server so that the SIP server will recognize if the device is in online status.
UDP Alive Msg Interval: The message-sending time interval ranges from 5 to 60 seconds. The default is 30 seconds.
RPort: Enable the RPort when the SIP server is in the WAN.
SNMP Setting
Simple Network Management Protocol(SNMP) is a protocol for managing IP network devices. It allows network administrators to monitor devices and receive alerts for attention-worthy conditions. SNMP provides variables describing system configuration, organized in hierarchies and described by Management Information Bases (MIBs).
To set it up, go to the Network > Advanced > SNMP interface.
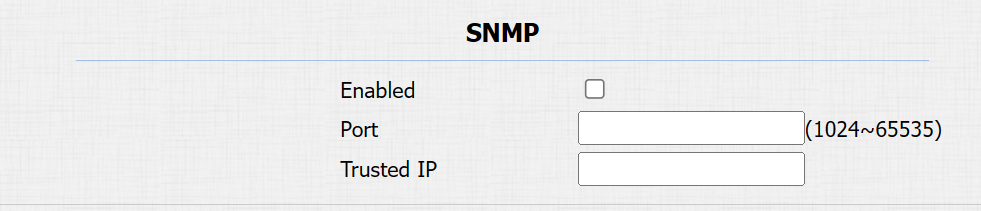
Trusted IP: The allowed SNMP server address. It can be an IP address or any valid URL domain name.
VLAN Setting
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a logical group of nodes from the same IP domain, regardless of their physical network segment. It separates the layer 2 broadcast domain via switches or routers, sending tagged packets only to ports with matching VLAN IDs. Utilizing VLANs enhances security by limiting ARP attacks to specific hosts and improves network performance by minimizing unnecessary broadcast frames, thereby conserving bandwidth for increased efficiency.
To set it up, go to the Network > Advanced > VLAN interface.

VID: The VLAN ID for the designated port.
Priority: The VLAN priority for the designated port.
TR069 Setting
TR-069 (Technical Report 069) provides the communication between Customer-Premises Equipment (CPE) and Auto-Configuration Servers (ACS). It includes both a safe auto configuration and the control of other CPE management functions within an integrated framework. For door phones, the administrators can manage all the devices on a common TR-069 Platform. IP phones can be easily and securely configured on the TR-069 platform to make mass deployment more efficient.
To set it up, go to the Network > Advanced > TR069 interface.
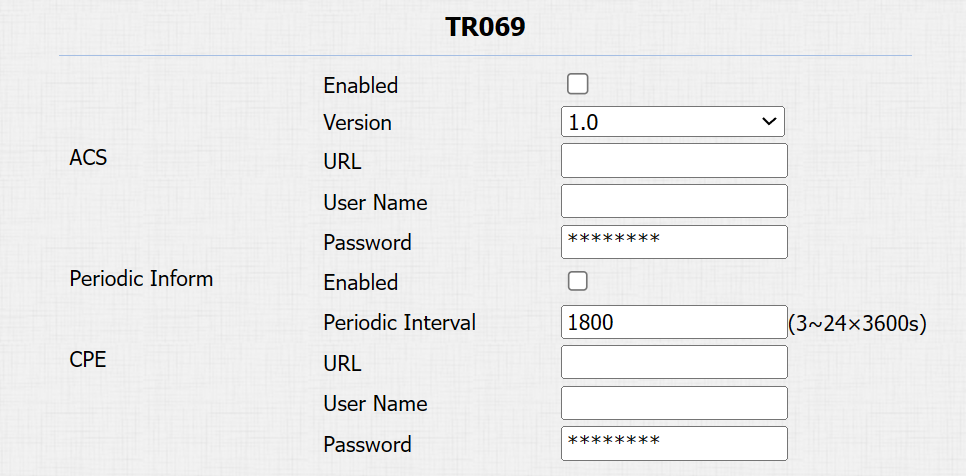
Version: Select the supported TR069 version (version 1.0 or 1.1).
ACS/CPE: ACS is short for auto-configuration servers on the server side, and CPE is short for customer-premise equipment, as client-side devices.
URL: The URL for ACS or CPE.
Periodic Interval: The interval for periodic notification.
Device Web HTTP Setting
This function manages device website access. The device supports two remote access methods: HTTP and HTTPS (encryption).
To set it up, go to the Network > Advanced > Web Server interface.
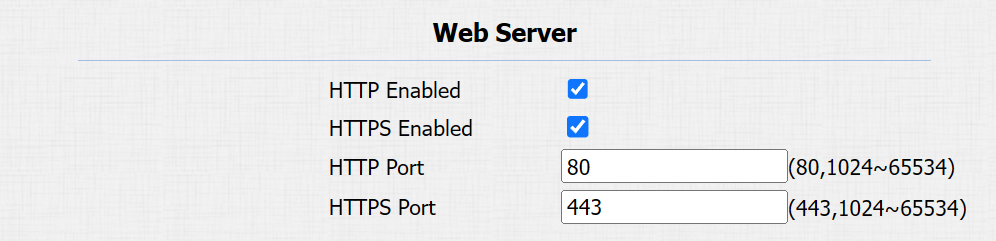
HTTP/HTTPS Enabled: HTTP and HTTPS are enabled by default.
HTTP/HTTPS Port: Specify the web server port for accessing the device web interface via HTTP/HTTPS.